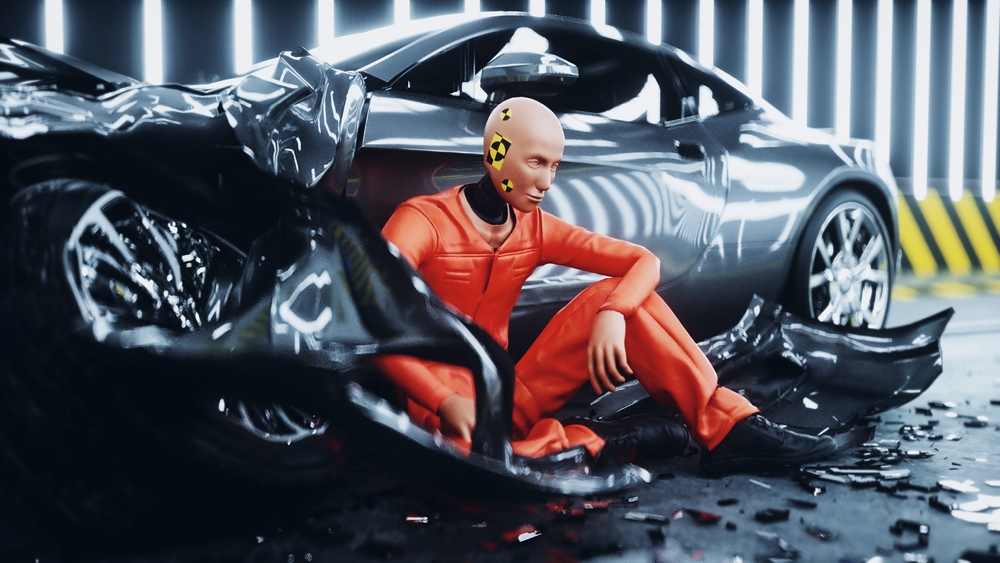
Before diving into the latest innovations, it’s essential to understand why car safety features are so vital. The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) reports that in 2020 alone, over 38,000 people died in motor vehicle crashes in the United States. Advanced safety features can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and improve the chances of survival in the event of a crash. They not only protect the vehicle’s occupants but also contribute to the safety of pedestrians and other road users.
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS)
One of the most significant advancements in car safety is the development of Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS). These systems use sensors, cameras, and radar to monitor the vehicle’s surroundings and assist the driver in making safer decisions. Some key components of ADAS include:
1. Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB)
AEB systems detect an imminent collision and automatically apply the brakes to prevent or mitigate the impact. This feature is particularly useful in city traffic where sudden stops are common.
2. Lane Departure Warning (LDW) and Lane Keeping Assist (LKA)
LDW alerts the driver if the vehicle begins to drift out of its lane, while LKA provides gentle steering inputs to keep the car within its lane. These systems are designed to reduce accidents caused by driver distraction or drowsiness.
3. Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC)
ACC maintains a set speed while automatically adjusting the distance to the vehicle ahead. It reduces the need for manual speed adjustments, enhancing comfort and safety during long drives.
4. Blind Spot Detection (BSD)
BSD uses sensors to monitor the vehicle’s blind spots and alerts the driver if another vehicle is detected. This feature is particularly valuable during lane changes.
5. Traffic Sign Recognition (TSR)
TSR systems use cameras to identify traffic signs and display the information on the dashboard. This helps drivers stay aware of speed limits and other important road signs.
Autonomous Driving Technology
Autonomous driving technology, while still in its developmental stages, promises to revolutionize road safety. Companies like Tesla, Waymo, and others are making significant strides in this area. Autonomous vehicles (AVs) use a combination of ADAS features, artificial intelligence, and machine learning to navigate and make decisions without human intervention. The goal is to reduce human error, which is a leading cause of accidents.
Levels of Autonomy
Autonomous driving technology is classified into five levels:
- Level 1: Driver Assistance – Basic features like ACC and LDW.
- Level 2: Partial Automation – Combines multiple ADAS features but requires driver supervision.
- Level 3: Conditional Automation – The car can handle most driving tasks, but the driver must be ready to take control.
- Level 4: High Automation – The car can drive itself in most conditions, with minimal driver intervention.
- Level 5: Full Automation – No driver needed; the car can handle all driving tasks.
Currently, most commercially available vehicles are at Level 2 or 3, but the industry is rapidly progressing toward higher levels of autonomy.
Enhanced Visibility and Night Vision
Driving at night or in adverse weather conditions can be challenging. Innovations in visibility and night vision aim to improve safety in such scenarios.
1. Adaptive Headlights
Adaptive headlights adjust their direction and intensity based on the vehicle’s speed, steering angle, and road conditions. They provide better illumination around curves and reduce glare for oncoming drivers.
2. Night Vision Systems
Night vision systems use infrared cameras to detect pedestrians, animals, and other obstacles beyond the reach of the headlights. The information is displayed on the dashboard, giving the driver more time to react.
3. High-Definition Cameras
High-definition cameras provide a clearer and wider view of the vehicle’s surroundings. They are used in features like rearview cameras, surround-view systems, and parking assistance.
Improved Airbag Systems
Airbags have been a standard safety feature for decades, but recent advancements have made them even more effective.
1. Multi-Stage Airbags
Multi-stage airbags deploy with varying force depending on the severity of the crash and the position of the occupants. This reduces the risk of injury from the airbag itself.
2. External Airbags
Some manufacturers are experimenting with external airbags that deploy outside the vehicle to cushion the impact during a collision. These are still in the experimental phase but hold great promise for future safety.
3. Smart Airbags
Smart airbags use sensors to detect the size, weight, and position of the occupants, adjusting their deployment accordingly. This ensures optimal protection for everyone in the vehicle.
Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Communication
V2X communication enables vehicles to exchange information with each other and with infrastructure like traffic lights and road signs. This technology can prevent accidents by providing real-time data about road conditions, traffic, and potential hazards.
Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V)
V2V communication allows cars to share information about their speed, position, and direction. This can help prevent collisions by alerting drivers to potential hazards.
Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I)
V2I communication connects vehicles to traffic signals, road signs, and other infrastructure. It can provide drivers with information about traffic conditions, road closures, and other important updates.
Vehicle-to-Pedestrian (V2P)
V2P communication uses smartphones and other devices to detect pedestrians and cyclists, alerting drivers to their presence. This can be particularly useful in urban areas with heavy foot traffic.
Enhanced Structural Integrity
Advancements in materials and engineering have led to stronger and more resilient vehicle structures.
High-Strength Steel and Aluminum
Modern cars use high-strength steel and aluminum to create a rigid but lightweight frame. This improves crash protection without adding unnecessary weight.
Crumple Zones
Crumple zones are designed to absorb and dissipate energy during a collision, reducing the impact on the occupants. Advances in computer modeling have optimized the design of these zones for maximum safety.
Advanced Restraint Systems
Modern restraint systems, including seatbelts and headrests, are designed to work in conjunction with airbags to provide comprehensive protection. Features like pre-tensioners and load limiters adjust the seatbelt’s tension to reduce injury during a crash.
Advanced Tire Technology
Tires are the only contact point between your vehicle and the road, making them crucial for safety. Recent advancements in tire technology are enhancing road grip, durability, and overall performance.
Run-Flat Tires
Run-flat tires allow you to drive a short distance even after a puncture, giving you the time to reach a safe location or a repair shop. This reduces the risk of being stranded in a dangerous area.
Self-Sealing Tires
Self-sealing tires contain a layer of sealant inside that automatically seals small punctures, maintaining tire pressure and preventing flats. This innovation enhances safety by ensuring that minor punctures do not lead to sudden blowouts.
All-Weather Tires
All-weather tires provide a balance of performance in both summer and winter conditions. They are designed to offer good traction on wet, dry, and snowy roads, making them an ideal choice for regions with varying weather patterns.
Smart Tires
Smart tires come equipped with sensors that monitor tire pressure, temperature, and tread depth. These sensors can send real-time data to the driver, alerting them to potential issues before they become serious problems. This proactive approach to tire maintenance can prevent accidents caused by tire failures.
Child Safety Innovations
Children are among the most vulnerable passengers in a vehicle. Recent innovations in child safety features are ensuring that young passengers are better protected.
ISOFIX and LATCH Systems
ISOFIX (International Standards Organisation FIX) and LATCH (Lower Anchors and Tethers for Children) systems make installing child car seats easier and more secure. These systems use standardized anchor points in the vehicle to ensure that the car seat is firmly attached.
Advanced Child Seats
Modern child car seats come with features like side-impact protection, adjustable headrests, and harnesses that grow with the child. Some seats are even equipped with sensors that alert the driver if the child seat is not properly secured.
Rear-Facing Seats
Experts recommend keeping children in rear-facing seats for as long as possible, as they provide better protection for the head, neck, and spine in the event of a crash. Recent designs have extended the weight and height limits for rear-facing seats, allowing children to stay in this safer position longer.
Child Safety Locks
Child safety locks on doors and windows prevent children from opening them accidentally while the vehicle is in motion. These locks are an essential feature for families with young children, ensuring that curious hands do not lead to dangerous situations.
Innovations in Car Lighting
Lighting plays a vital role in road safety, providing visibility and signaling intentions to other road users. Recent innovations in car lighting technology are making driving safer for everyone.
LED and Laser Headlights
LED (Light Emitting Diode) and laser headlights offer brighter and more focused beams compared to traditional halogen lights. They provide better illumination of the road ahead, especially in low-light conditions, and consume less energy.
Adaptive Lighting Systems
Adaptive lighting systems adjust the direction and intensity of the headlights based on the vehicle’s speed, steering angle, and road conditions. These systems improve visibility around curves and reduce glare for oncoming drivers, enhancing overall safety.
Automatic High Beams
Automatic high beams use sensors to detect oncoming traffic and adjust the headlights accordingly. This feature ensures optimal illumination without blinding other drivers, making nighttime driving safer.
Dynamic Turn Signals
Dynamic turn signals use a series of lights that illuminate sequentially, clearly indicating the direction of the turn. This enhances communication between drivers and reduces the likelihood of accidents caused by unclear signaling.
Cybersecurity in Modern Vehicles
As vehicles become more connected and reliant on software, cybersecurity has become a critical aspect of car safety. Protecting your vehicle from cyber threats is essential for ensuring both safety and privacy.
Secure Communication Protocols
Modern vehicles use secure communication protocols to protect data transmitted between the vehicle and external devices or networks. These protocols encrypt data to prevent unauthorized access and ensure the integrity of the information.
Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates
OTA updates allow manufacturers to remotely update a vehicle’s software, fixing bugs and improving performance without requiring a visit to the dealership. This ensures that the vehicle is always running the latest and most secure software.
Intrusion Detection Systems
Intrusion detection systems monitor the vehicle’s network for unusual activity that could indicate a cyber attack. These systems can alert the driver and take preventative measures to protect the vehicle’s critical systems.
Privacy Protection
With the increasing use of data in connected vehicles, protecting the privacy of the driver and passengers is paramount. Manufacturers are implementing strict data privacy measures to ensure that personal information is kept secure and only used with the owner’s consent.
Enhanced Safety for Electric Vehicles (EVs)
Electric vehicles (EVs) are becoming more popular due to their environmental benefits and technological advancements. Recent innovations are enhancing the safety of EVs, making them a viable option for more drivers.
Battery Safety
Battery safety is a primary concern for EVs. Manufacturers are developing advanced battery management systems that monitor the health of the battery, prevent overheating, and ensure safe charging and discharging cycles. This reduces the risk of battery fires and extends the lifespan of the battery.
Crash Safety
EVs are designed with crash safety in mind. Many EVs have a low center of gravity due to the placement of the battery pack, which improves stability and reduces the risk of rollovers. Additionally, the absence of a traditional engine allows for larger crumple zones to absorb impact energy during a collision.
Pedestrian Safety
EVs are quieter than traditional vehicles, which can pose a risk to pedestrians who may not hear them approaching. To address this, manufacturers are equipping EVs with pedestrian warning sounds that activate at low speeds, alerting pedestrians to the vehicle’s presence.
Advanced Driver Assistance for EVs
Many EVs come equipped with advanced driver assistance features, such as automatic emergency braking, lane-keeping assist, and adaptive cruise control. These features enhance safety by assisting the driver in maintaining control and avoiding accidents.